TIN 또는 Terrain 데이터 생성 고려사항
지난 시간에 이어 TIN 구축시 고려해야 할 사항을 알아보기로 한다. ArcGIS의 경우 TIN을 구축하여 래스터로 변환할 수도 있지만 GeoDatabase(File GeoDatabase, SDE 등)를 사용할 경우 Terrain 데이터셋을 사용하면 데이터 편집 및 유지관리에 있어 효율적이다.
1. 들어가기 전에
Terrain 데이터셋을 한마디로 표현하자면 Multi-Resolution TIN이다. Terrain 데이터셋은 지오데이터베이스 내의 피쳐로 저장된 측정데이터로부터 구축, 관리된다.
- 지오데이터베이스에서 관리되는 데이터셋 저장구조
- 지형을 표현하기 위해 TIN 데이터 구조 사용
- 다중 해상도를 표현하기 위해 피라미드를 사용
- 여기에 대해서는 다음차에 부가 설명하기로 한다.
여기에서는 데이터 구축관점에서 TIN 및 Terrain을 같은 의미로 사용하기로 한다.
2. Surface feature type (SFType)
피쳐클래스(Feature Class)는 Terrain 데이터셋을 구축하기 위한 데이터 소스를 제공한다. Terrain 데이터셋 설계시 각각의 데이터 소스(피쳐 클래스)가 어떤 역할을 할 것인지를 결정해야 한다. 이 역할을 Surface Feature Type(SFType)이라 부른다.
여기에는 Mass Points, Breaklines, Polygon 유형이 있다. Breaklines과 Polygon은 Hard 및 Soft 조건이 있다. Soft는 지형을 완만(smoothly)하게, Hard는 급격하게(discontinuity) 표현한다.
포인트와 멀티포인트 피쳐클래스는 Mass Points로만 사용될 수 있으며, 폴리라인과 폴리곤은 다음의 역할을 수행할 수 있다.
- Breaklines
- Clip polygons
- Erase polygons
- Replace polygons
- Value fill polygons
▣ Mass points
Mass Points는 TIN에서 노드로 사용되는 데이터 소스로 LiDAR와 같은 여러 가지 새로운 센서들은 고해상도의 Terrain 데이터셋을 생성하는데 사용되는 대량의 Mass Points를 취득할 수 있다.
LiDAR로부터 취득되는 LAS와 같은 데이터 파일 포맷은 Multipoint 피쳐 클래스로 지오데이터베이스에 탑재될 수 있으며 Geoprocessing 도구를 사용할 수 있다. 수치지도에서는 표고점을 사용할 수 있다.

Breakline은 일반적으로 능선이나 하천과 같은 자연 지형이나 도로와 같은 인공지물을 표현하는데 사용한다. 아래는 라인을 구성하는 각 버텍스마다 고도값(Z)을 가진 Breakline을 보여주며, TIN을 구성할 때 하나 이상의 Triangle Edge로 변환된다.

▣ Clipping polygons
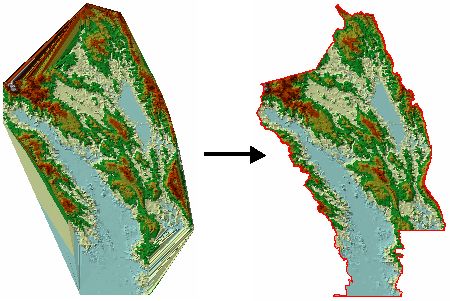
Clipping Polygon은 Terrain에서 경계를 정의하는데 사용되며, 구축할 지역이 불규칙한 영역일 경우 Clip Polygon을 적용하지 않으면 Convex 모양을 나타낸다.
아래 그림에서 왼쪽은 클립되지 않은 상태이며, 측정 데이터가 없는 지역까지 Terrain이 구축되어 있어 오류가 발생한다. Clip Polygon을 이용하면 연구지역만을 대상으로 구축하거나 수집된 측정지역만을 대상으로 Terrain 데이터셋을 구축할 수 있다.
▣ Erase polygons

Replace Polygon은 일정한 높이의 영역을 정의하는데 사용하며, 일반적으로 호수나 평평한 인공구조물을 표현하는데 사용한다. Replace Polygon은 다른 고도값을 가진 데이터가 내부에 있을 경우 이를 무시하고 재정의하는데 최적으로 사용될 수 있다.
만약 이 영역 내에서 고도값이 일정하다면 Replace Polygon을 사용하는 대신 Breakline을 사용하면 TIN을 구성할 때 속도 및 처리 면에서 효율적이다.

▣ Value fill polygons
Value fill polygon은 Terrain 데이터셋의 Triangle에 정수값(tag value)를 설정하는데 사용된다.
Terrain은 이 triangle의 tag값을 이용하여 사용자 정의 심볼로 렌더링 가능하다.
▣ Hard or soft surface feature types (SFTypes)
위에서 언급했듯이 라인과 폴리곤 피쳐 유형에서 Hard 및 Soft 조건은 그 위치에서의 지형의 평탄하거나 연속적인 지형의 변화를 나타내는데 사용된다. 이 정보는 Natural neighbor 보간법에 영향을 주며, Hard line과 hard Poygon을 제외하고는 지형을 부드럽게 처리한다.
Natural neighbor 보간법은 Terrain을 래스터로 변환, TIN을 래스터로 변환, shape을 보간하는 도구에 사용된다. 매스 포인트를 제외한 모든 SFType은 Hard 또는 Soft 조건을 지원한다.
일반적으로 Hard Breakline은 해안선, 하천, 댐, 건축물 흔적, 도로경계, 도로절토 등에서 사용하며, Soft Breakline은 연구지역 경계, 부드럽고 완만한 능선과 계곡, 데이터가 없는 영역의 경계, 등고선(등고선은 매스 포인트로 사용이 가능함) 등에서 사용한다.
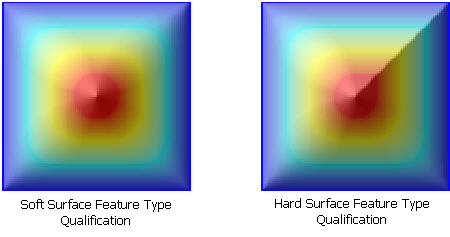
아래 두 그림을 살펴보자. 두 그림 모두 Terrain 으로부터 Natural neighbor 보간을 사용하여 생성한 래스터이다.
단지, 왼쪽은 모든 라인을 soft line으로 추가하여 Terrain을 구성하였으며, 오른쪽 그림은 우상단 모서리에 대각선의 Hard breakline을 추가한 경우이다.
3. Types of source data supported in terrain datasets
다음 표는 ArcGIS Desktop Help에 정리되어 있는 Surface Feature Type의 예이다. 정리가 잘 되어 있으므로 한번씩 확인 하기 바랍니다.
▣ Common types of data used to build terrains
- Photogrammetrically derived mass points
- Photogrammetrically derived breaklines
- GPS points
- Lidar points
- Sonar
- Contour lines
- Points, lines, polygons (mass, break, clip, erase, replace)
▣ Surface feature types in terrain datasets
|
Surface feature type |
Feature class |
Z-value source in the
feature class |
Thematic data type examples |
|
Mass points (x,y,z locations) |
Point |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per point Attribute column holding a z-value for each point |
Spot heights Survey points GPS points |
|
Multipoint |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per point
Attribute column holding one
z-value per shape |
Lidar points Sonar points |
|
|
Line |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per vertex Attribute column holding one z-value per shape |
Contours |
|
|
Polygon |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per
vertex Attribute column holding one
z-value per shape |
Shoreline delineation |
|
|
Breaklines (hard or soft) |
Line |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per vertex Attribute column holding one z-value per shape No height source; z-values interpolated for each feature from the
surface before being added |
Contours Edge of pavement Roads Waterlines (streams, rivers, canals, shorelines) |
|
Polygon |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per
vertex Attribute column holding one
z-value per shape (such as a shoreline) No height source; z-values
interpolated for each feature from the surface before being added |
Lake shoreline |
|
|
Clipping polygons (hard or soft) |
Polygon |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per vertex Attribute column holding one z-value per shape (such as a shoreline) No height source; z-values interpolated for each feature from the
surface before being added |
Study area boundary |
|
Erase polygons (hard or soft) |
Polygon |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per
vertex Attribute column holding one
z-value per shape No height source; z-values
interpolated for each feature from the surface before being added |
Lake shorelines Obscured areas (dense forest canopy) |
|
Replace polygons (hard or soft) |
Polygon |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per vertex Attribute column holding one z-value for all vertices in each shape |
Water bodies |
|
Value Fill (hard or soft) |
Polygon |
Shape geometry; x,y,z per
vertex No height source; z-values interpolated for each feature from the
surface before being added |
Land-use codes |
※ 참고문헌
- ArcGIS Desktop Help

댓글
댓글 쓰기